Difference between revisions of "Sensors & Circuits"
From CCRMA Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Hall Effect== | ==Hall Effect== | ||
[http://www.sensorwiki.org/index.php/Hall_effect Hall Effect] on Sensorwiki.org | [http://www.sensorwiki.org/index.php/Hall_effect Hall Effect] on Sensorwiki.org | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==IR Distance== | ==IR Distance== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Reflective Optical Sensor=== | ===Reflective Optical Sensor=== | ||
Revision as of 08:24, 27 June 2007
Hall Effect
Hall Effect on Sensorwiki.org
IR Distance
Reflective Optical Sensor
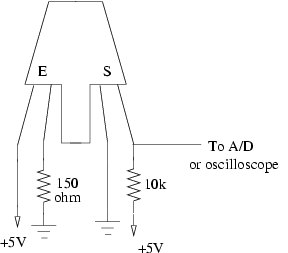
The reflective optical sensor ( Datasheet ) consists of an infrared LED, labelled "E" for Emitter on the diagrand and on the package, and a phototransistor that passes an amount of current proportional to the reflected light received. The phototransistor is labelled "S" for Sensor. The one leg of the sensor is connected to +5V, which supplies current, and the voltage drop across the 10k resistor that we measure is proportional to the amount of current.
There is a continuous voltage response for objects over a short range of proximity to the sensor. The response is not linear. Linearity can be approximated by the log of the log of the signal.